Unit III
Communication, collaboration and media literacy
3.1
Component of Communication
There are several components of communication. These include:
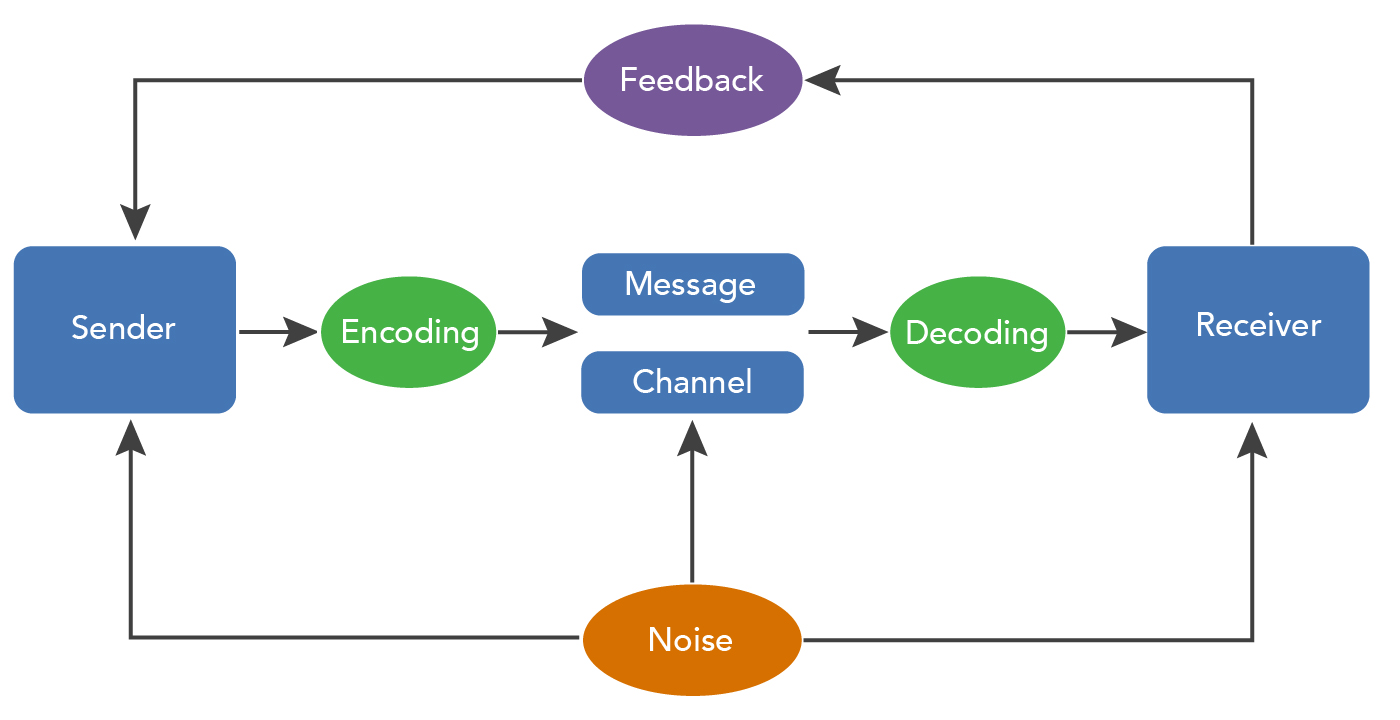
Sender: The person who initiates the communication process by encoding a message and sending it to the receiver.
Message: The information or content that the sender wants to communicate to the receiver.
Channel: The medium or mode of transmission that the sender uses to send the message to the receiver, such as speech, text, or email.
Receiver: The person who receives the message and decodes it to understand the information conveyed by the sender.
Feedback: The response or reaction of the receiver to the message. Feedback can be verbal or nonverbal and can help the sender to understand whether the message was received and understood correctly.
Context: The situation, environment, or background in which the communication takes place. The context can influence the way the message is interpreted by the receiver.
Noise: Any interference or distortion that affects the communication process, such as physical noise, psychological noise, or semantic noise. Noise can make it difficult for the sender and receiver to communicate effectively.
3.2 Types of communication media
There are several types of communication media that can be used to transmit messages between individuals or groups. Some common types of communication media include:
Verbal Communication Media: This includes face-to-face communication, telephone conversations, and video conferencing.
Written Communication Media: This includes emails, memos, letters, reports, and instant messaging.
Visual Communication Media: This includes charts, graphs, diagrams, pictures, and videos.
Electronic Communication Media: This includes social media platforms, blogs, websites, and podcasts.
Nonverbal Communication Media: This includes body language, facial expressions, gestures, and tone of voice.
Mass Communication Media: This includes television, radio, newspapers, magazines, and the internet.
Interpersonal Communication Media: This includes one-on-one conversations, group meetings, and discussions.
The choice of communication media depends on various factors such as the nature of the message, the audience, the purpose of the communication, and the available resources.
3.3 Concept of collaboration
Collaboration is the act of working together with others to achieve a common goal or purpose. It involves individuals or groups working together to share ideas, knowledge, and skills in order to achieve a shared outcome. Collaboration is an essential component of many workplaces and is increasingly important in a globalized and interconnected world.
Collaboration requires communication, trust, mutual respect, and shared responsibility. It involves identifying the strengths and weaknesses of each team member and leveraging them to achieve a common goal. Collaboration can take many forms, such as brainstorming sessions, group projects, team-building exercises, and cross-functional teams.
Effective collaboration can have several benefits, including:
Increased productivity and efficiency: Collaboration allows individuals to work together to achieve a common goal, which can result in faster and more efficient work.
Improved problem-solving: Collaboration allows individuals to share ideas and perspectives, which can lead to more creative and effective solutions.
Increased innovation: Collaboration allows individuals to draw on the strengths and experiences of others, which can lead to new ideas and approaches.
Improved relationships: Collaboration fosters a sense of teamwork and camaraderie, which can lead to stronger relationships and better communication.
Enhanced learning: Collaboration allows individuals to learn from each other and share knowledge, which can lead to personal and professional growth.
Overall, collaboration is a powerful tool that can help individuals and organizations achieve their goals more effectively and efficiently.
3.4 Social media and collaboration
practices
Social media has become an increasingly popular tool for collaboration in both personal and professional contexts. Social media platforms provide a range of features and tools that facilitate communication, information sharing, and collaboration among individuals and groups. Some of the ways social media can support collaboration practices include:
Communication: Social media platforms allow individuals and teams to communicate and share information in real-time, regardless of location. This can support more efficient collaboration and decision-making.
Knowledge sharing: Social media platforms allow individuals and groups to share knowledge, expertise, and resources. This can help to promote learning and innovation within organizations.
Team building: Social media platforms can be used to facilitate team-building activities, such as virtual team-building exercises, group chats, and online collaboration spaces.
Crowdsourcing: Social media platforms can be used to engage a wider community in problem-solving and decision-making processes, through techniques such as crowdsourcing and open innovation.
Networking: Social media platforms can be used to connect individuals with similar interests or areas of expertise, enabling them to collaborate and share knowledge.
Project management: Social media platforms can be used to manage projects and workflows, allowing teams to collaborate more effectively and efficiently.
However, it is important to note that the use of social media for collaboration practices also raises issues related to privacy, security, and information management. Organizations should establish policies and procedures to ensure that social media is used appropriately and responsibly. They should also ensure that individuals are trained on the safe and effective use of social media for collaboration purposes.
3.5 Classroom collaboration
Classroom collaboration is a teaching approach that involves students working together in groups to achieve a common goal or complete a task. It can be used to promote active learning, critical thinking, and problem-solving skills, while also fostering social and emotional development.
Classroom collaboration can take many forms, such as group discussions, debates, projects, and presentations. Some of the benefits of classroom collaboration include:
Improved academic achievement: Collaboration allows students to share knowledge and expertise, which can lead to a deeper understanding of the subject matter and improved academic performance.
Enhanced social and emotional development: Collaboration encourages students to develop communication, teamwork, and leadership skills, while also fostering empathy and respect for others.
Increased engagement and motivation: Collaboration can make learning more fun and engaging, which can help to increase student motivation and interest in the subject matter.
Improved problem-solving and critical thinking: Collaboration encourages students to think creatively and critically, as they work together to solve problems and complete tasks.
Diverse perspectives: Collaboration allows students to learn from one another, and to gain exposure to different perspectives and approaches to problem-solving.
To facilitate effective classroom collaboration, teachers should provide clear instructions and expectations, assign roles and responsibilities within groups, and monitor and support student progress. They should also create a positive and inclusive classroom environment, where students feel comfortable sharing their ideas and working together.
3.6 Concept of media literacy for
learner
Media literacy is the ability to critically analyze and evaluate media messages, as well as to create media content in a responsible and effective manner. In today's digital age, media literacy is an essential skill for learners of all ages, as they are constantly exposed to various forms of media, including social media, news, advertisements, and entertainment.
Media literacy enables learners to become informed and engaged media consumers, who are able to recognize and avoid biased or misleading information, and to make informed decisions based on reliable sources of information. It also empowers learners to become creators of media content, using tools and platforms to express themselves, share their ideas, and connect with others.
Some key components of media literacy for learners include:
Understanding media messages: Learners should be able to analyze and interpret media messages, including recognizing persuasive techniques and bias.
Evaluating sources: Learners should be able to assess the credibility and reliability of sources, including identifying fake news and misinformation.
Creating media content: Learners should be able to use media tools and platforms to create content, such as videos, podcasts, and social media posts, while also understanding issues such as copyright and fair use.
Engaging in digital citizenship: Learners should be able to participate responsibly in online communities, respecting others' rights and privacy, and avoiding cyberbullying and other harmful behaviors.
By developing media literacy skills, learners are better equipped to navigate the complex and ever-changing media landscape, while also developing the critical thinking and communication skills that are essential for success in the 21st century.
3.7 Digital citizen and netiquettes
Here are 9 elements of digital citizenship and netiquette:
Respect - Digital citizens should respect the rights and privacy of others, as well as the laws and regulations that govern online behavior.
Responsibility - Digital citizens should be responsible for their own actions online, and take steps to protect their privacy and security.
Trustworthiness - Digital citizens should be honest and trustworthy in their online interactions, and avoid spreading false information or engaging in deception.
Citizenship - Digital citizens should be active and engaged members of online communities, contributing positively and responsibly to discussions and debates.
Self-control - Digital citizens should exercise self-control in their use of technology, avoiding addictive behaviors and using technology in ways that promote personal growth and well-being.
Media literacy - Digital citizens should be able to critically evaluate and interpret media messages, and seek out reliable sources of information.
Digital footprint - Digital citizens should be aware of their digital footprint, and take steps to manage and protect their online reputation.
Security - Digital citizens should take steps to protect their personal and financial information, as well as their devices and accounts, from cyber threats.
Netiquette - Digital citizens should follow basic rules of online behavior, such as using appropriate language and tone, avoiding spamming and trolling, and respecting the opinions and perspectives of others.
Practicing good netiquette involves following some basic rules of online behavior, such as:
Being polite and respectful: This includes avoiding offensive language, sarcasm, or aggressive behavior, and using appropriate language and tone in online communication.
Using appropriate language and tone: Digital citizens should avoid using all caps, excessive exclamation marks, or other forms of online shouting or exaggeration.
Using proper grammar and spelling: This helps to ensure that communication is clear and easy to understand.
Avoiding spamming or trolling: Digital citizens should avoid posting irrelevant or repetitive content, or engaging in disruptive behavior such as trolling or flaming.
By being a responsible digital citizen and practicing good netiquette, individuals can help to create a positive and productive online community, while also protecting their own privacy and security.
3.8 Application of create, publish,
share audio, video materials.
Creating, publishing, and sharing audio and video materials can be a powerful tool for communication and expression in a variety of contexts. Here are some examples of how these tools can be applied:
Education: Teachers and students can create audio and video materials, such as podcasts and educational videos, to enhance learning and share knowledge with others.
Marketing and advertising: Businesses can use audio and video materials to promote their products and services, and engage with customers in creative and memorable ways.
Entertainment: Musicians, filmmakers, and other artists can create and share audio and video materials, such as music videos and short films, to showcase their talents and reach a wider audience.
Journalism: Journalists and news organizations can use audio and video materials to report on important events and issues, and to provide context and analysis to their audiences.
Personal expression: Individuals can create and share audio and video materials to express themselves creatively, share their experiences and perspectives, and connect with others who share their interests.
When creating, publishing, and sharing audio and video materials, it is important to consider ethical and legal considerations, such as obtaining consent from those who appear in the content, respecting copyright and intellectual property rights, and avoiding harmful or offensive content. Additionally, it is important to use appropriate tools and platforms to share content, and to ensure that it is accessible to all audiences, regardless of their abilities or backgrounds.
3.9 Classroom activities on publishing students portfolios in online
Publishing student portfolios online can be a great way to showcase their work, promote their achievements, and encourage collaboration and feedback from peers and educators. Here are some classroom activities that could be used for publishing students portfolios online:
Portfolio creation: Students can be given the opportunity to create their own portfolios, which could include a range of materials such as written work, photos, videos, and artwork. They could also be given guidelines on what should be included in their portfolio, and how it should be organized.
Peer review: Students can review and provide feedback on each other's portfolios. This could be done through a structured feedback form or rubric, or through informal discussions and comments.
Reflection and self-assessment: Students can reflect on their own learning and progress, and assess their own work as they create their portfolio. This can help them to identify areas of strength and weakness, and set goals for future learning.
Showcase event: The portfolios could be showcased in an online event, such as a virtual gallery or presentation. This could be open to the school community or a wider audience, and could be an opportunity for students to receive recognition for their achievements.
Guest speaker or expert feedback: Students could receive feedback and advice from experts or guest speakers in their field of study, which could help them to refine their portfolios and develop their skills further.
Collaborative projects: Students could work collaboratively on a project, such as creating a group portfolio, to develop teamwork and collaboration skills. This could also encourage students to support and learn from each other.
When publishing student portfolios online, it is important to consider ethical and legal considerations, such as obtaining consent from students and their parents or guardians, and ensuring that the privacy and security of student information is protected. Teachers should also provide guidelines and training on appropriate online behavior and netiquette .





No comments:
Post a Comment